How to Maintain Good Posture to Avoid Strain sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. Good posture is not merely an aesthetic concern; it plays a critical role in our overall health and well-being. Many may underestimate its importance, often overlooking how poor posture can lead to discomfort, pain, and long-term health issues.
This discussion aims to illuminate the concept of good posture, debunk common misconceptions, and explore its relationship with daily activities.
As we delve deeper into this topic, we will uncover the various causes of poor posture, ranging from lifestyle choices to the impact of technology. Furthermore, we will provide practical techniques and exercises that can be easily integrated into your routine to promote better posture. With a focus on ergonomics and mindfulness, this narrative will equip you with the knowledge to develop and maintain good posture, ultimately enhancing your quality of life.
Understanding Posture
Maintaining good posture is essential for overall well-being and can significantly influence daily activities and health outcomes. Good posture is defined as the proper alignment of body parts, which ensures the least amount of strain on muscles and ligaments while minimizing the risk of injury. It plays a critical role in physical fitness, mental health, and productivity.Good posture is not merely about the position of the body while standing; it encompasses how we sit, walk, and even sleep.
Many individuals overlook the significance of maintaining proper alignment, often leading to discomfort and various health issues. Furthermore, some misconceive posture as merely a cosmetic concern. However, it is much more than that; it is foundational to maintaining musculoskeletal health and preventing chronic pain conditions.
Common Misconceptions about Posture
There are several misconceptions about posture that can lead to inadequate understanding and poor habits. These misconceptions often stem from a lack of awareness regarding the complexities of body mechanics.
- Posture is only important for people with back pain: Many believe that posture only matters if one experiences pain, but improper alignment can cause long-term damage even without immediate symptoms.
- Good posture is purely standing straight: While standing straight is a part of good posture, true alignment involves a comprehensive approach that includes sitting, moving, and even sleeping ergonomically.
- Good posture means forcing the back into a rigid position: Maintaining good posture does not involve rigidity; it requires balance and relaxation of muscles, allowing the body to be both aligned and comfortable.
Understanding these misconceptions helps individuals cultivate better posture habits and improves their overall health.
Posture and Overall Health
The relationship between posture and health is significant and multifaceted. Proper posture contributes to several physiological aspects, including respiratory efficiency, digestive function, and even mental clarity. When the spine and other body parts are correctly aligned, the body’s systems function optimally. For instance, good posture can enhance lung capacity, which in turn improves oxygen intake and energy levels. Furthermore, when seated or standing correctly, the pressure on the intervertebral discs is minimized, reducing the risk of chronic pain or injury.
The alignment of the body is crucial not only for physical comfort but also for mental well-being. A confident posture can enhance mood and promote a positive self-image.
In the workplace, maintaining ergonomic posture can lead to increased productivity and decreased absenteeism. Studies have shown that individuals who prioritize their posture experience fewer headaches and musculoskeletal disorders, contributing to a healthier work environment.Incorporating posture awareness into daily routines can result in long-term health benefits. Simple adjustments such as adjusting the height of a workstation, using supportive chairs, and practicing stretching exercises can significantly transform one’s posture and, by extension, their overall health.
Causes of Poor Posture

Poor posture is often a result of various lifestyle factors, environmental influences, and physical conditions. Understanding these causes is essential in addressing and improving posture for overall well-being. Factors contributing to poor posture can originate from daily habits, the use of technology, and certain medical conditions that may go unnoticed until they lead to significant discomfort or pain.
Lifestyle Factors Contributing to Poor Posture
A sedentary lifestyle is a primary contributor to poor posture. Prolonged periods of sitting, particularly in environments that lack ergonomic furniture, can lead to muscular imbalances and discomfort. Common lifestyle factors include:
- Extended sitting at desks without proper support, leading to slouching.
- Inadequate physical activity which weakens core muscles essential for maintaining an upright position.
- Improper lifting techniques that can strain the back and promote poor spinal alignment.
Incorporating regular exercise and mindful movements can significantly enhance posture and reduce strain.
Impact of Technology and Screen Time on Posture
The increasing reliance on digital devices has profoundly impacted posture. Prolonged screen time often leads individuals to adopt unhealthy positions, which can exacerbate the risk of developing poor posture. The following points illustrate how technology affects posture:
- Looking down at smartphones or tablets can cause neck strain, commonly referred to as “tech neck.” This condition results from repeatedly bending the neck forward, which over time can lead to chronic pain.
- Extended use of computers without proper monitor placement can encourage leaning forward or slouching, increasing back and shoulder discomfort.
- Gaming and prolonged use of laptops on couches or beds often result in awkward body positions that contribute to postural issues.
Being aware of these risks is vital in creating a more ergonomic and health-conscious tech environment.
Physical Conditions Leading to Poor Posture
Certain physical conditions can predispose individuals to poor posture, often making it difficult to maintain an optimal alignment of the spine. Common conditions include:
- Scoliosis, or an abnormal curvature of the spine, can significantly affect an individual’s ability to maintain proper posture.
- Muscle imbalances, where some muscles are too tight while others are too weak, can lead to compensatory postures for balance.
- Joint problems such as arthritis can limit mobility and lead to protective postures that may not be ideal.
Addressing these conditions through professional guidance can help in restoring alignment and improving overall posture.
Techniques for Maintaining Good Posture
Maintaining good posture is crucial for overall health and well-being. Proper posture not only helps to prevent discomfort and strain but also enhances productivity and confidence. This section Artikels effective techniques for maintaining good posture in various situations, particularly at a desk, during exercise, and while walking or standing.
Proper Sitting Posture at a Desk
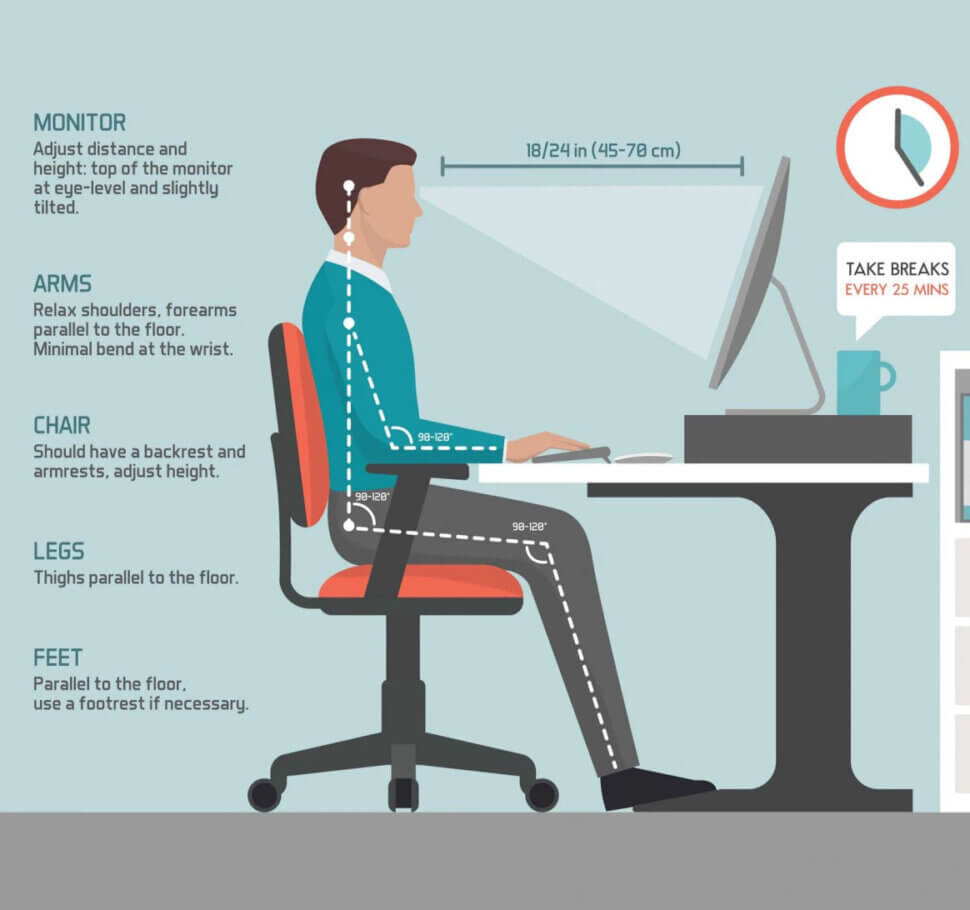
Sitting for extended periods can contribute to poor posture and associated discomfort. To ensure you maintain proper posture while seated, follow these step-by-step guidelines:
1. Adjust Your Chair
Sit in a chair that supports your lower back. The height should allow your feet to rest flat on the floor, and your knees should be at or slightly below hip level.
2. Position Your Monitor
Place your computer monitor at eye level, approximately an arm’s length away. This will help you keep your neck in a neutral position.
3. Use a Footrest
If your feet do not touch the floor, use a footrest to support them. This helps maintain a comfortable position and reduces strain on your legs.
4. Keep Your Arms Supported
Your elbows should be close to your body and form an angle between 90-120 degrees while typing. Use armrests if necessary to alleviate shoulder strain.
5. Maintain a Neutral Spine
Sit back in your chair with your back straight and shoulders relaxed. Your back should be aligned with the backrest of the chair.
Exercises that Promote Good Posture
Incorporating specific exercises into your routine can significantly enhance your posture and overall strength. The following exercises are designed to strengthen the muscles that support good posture:
Wall Angels
Stand with your back against a wall. With your arms at 90 degrees, slowly raise them while maintaining contact with the wall. This exercise helps to strengthen the upper back and shoulder muscles.
Plank
Hold a plank position for 30 seconds to a minute, ensuring your body forms a straight line from head to heels. This exercise strengthens the core, which is vital for maintaining good posture.
Cat-Cow Stretch
Position yourself on hands and knees. Inhale as you arch your back (cat), and exhale while lowering your belly and lifting your head (cow). This dynamic stretch increases flexibility and awareness of spinal alignment.
Maintaining Posture While Walking and Standing
Proper posture while walking and standing is essential for reducing strain and improving balance. Here are tips to help you maintain good posture in these activities:
Standing Tall
Stand with your feet hip-width apart. Distribute your weight evenly on both feet and keep your shoulders back and relaxed. Engage your core muscles gently.
Walking with Purpose
While walking, keep your head up and look forward, not down. Your arms should swing naturally at your sides, and your stride should be even and comfortable.
Mind Your Head
Avoid leaning your head forward; instead, keep it aligned with your spine. This helps to reduce neck strain and encourages a balanced stance.By applying these techniques and exercises, individuals can effectively maintain good posture, alleviate discomfort, and promote overall health and wellness.
Ergonomics and Workspace Setup

An ergonomic workspace setup is essential for promoting good posture and minimizing physical strain during work. By designing an environment that supports the body’s natural alignment, individuals can enhance their comfort, productivity, and overall well-being. This segment will focus on the importance of chair and desk height, as well as the organization of tools and equipment, to encourage proper posture.
Designing an Ergonomic Workspace Layout
Creating an ergonomic workspace layout involves careful consideration of furniture and equipment placement to promote good posture. The following elements are crucial in designing an effective workspace:
- Desk Height: A desk that is at elbow height when seated allows for optimal arm positioning, reducing strain on the shoulders and neck.
- Chair Selection: An adjustable chair with lumbar support is vital for maintaining the natural curve of the spine, thus preventing back strain.
- Monitor Position: The top of the monitor screen should be at or just below eye level to minimize neck strain and encourage a neutral head position.
- Keyboard and Mouse Placement: These should be positioned at a height where the elbows are at a 90-degree angle to keep the wrists in a neutral position, preventing repetitive strain injuries.
Importance of Chair and Desk Height in Maintaining Posture
Proper chair and desk height is integral to maintaining an ergonomic posture during work. It enables the body to align naturally and reduces the risk of discomfort or injury.Consider the following points:
- Adjustability: A chair that can be adjusted in height allows users to find their optimal sitting position, which should ideally have their feet flat on the ground and knees at hip level.
- Support: A well-designed chair with proper lumbar support encourages users to sit back and utilize the chair’s support, which can help sustain spinal alignment and reduce fatigue.
- Desk Clearance: The desk should have enough clearance for the knees and thighs while seated, which can prevent pressure points and irritation.
Organizing Tools and Equipment for Proper Posture Usage
The arrangement of tools and equipment within the workspace plays a significant role in promoting good posture. An organized workspace reduces unnecessary movements and encourages efficient body mechanics.To achieve this:
- Accessibility: Frequently used items should be within easy reach to avoid excessive stretching or twisting, which can lead to strain.
- Ergonomic Accessories: Using items such as a document holder can help keep materials at eye level, thus reducing neck strain from looking down.
- Footrests: A footrest can enhance comfort for shorter individuals and help maintain proper leg positioning, preventing discomfort during long periods of sitting.
“An ergonomic workspace promotes not only comfort but also productivity by minimizing the risk of injury and strain.”
Stretching and Strengthening Exercises
Maintaining good posture is significantly influenced by the flexibility and strength of our muscles. Incorporating a routine of stretching and strengthening exercises can enhance our posture, alleviate strain, and promote overall musculoskeletal health. Regularly engaging in these exercises not only combats the effects of poor posture but also contributes to a more active and energetic lifestyle.Stretching exercises play a crucial role in improving flexibility, which is vital for maintaining an optimal range of motion in the joints.
Strengthening exercises, on the other hand, focus on building the muscles that support the spine and core, thereby enhancing stability and posture. It is essential to incorporate both types of exercises into a regular fitness routine to achieve the best results.
Stretches to Improve Flexibility and Posture
Incorporating specific stretches into your daily routine can significantly enhance flexibility, which in turn supports better posture. Below are recommended stretches that target key muscle groups:
- Chest Stretch: Stand with your arms out to the sides and gently pull back, opening your chest. This stretch combats rounded shoulders.
- Neck Stretch: Gently tilt your head to one side, bringing your ear towards your shoulder. Hold for 15-30 seconds on each side to relieve neck tension.
- Cat-Cow Stretch: On all fours, alternate between arching your back towards the ceiling and sinking it towards the floor. This stretch promotes spinal flexibility.
- Seated Forward Bend: While sitting, extend your legs and reach towards your toes. This stretch lengthens the spine and hamstrings.
- Hip Flexor Stretch: Lunge forward with one leg while keeping the other knee on the ground. This stretch releases tight hip flexors that can contribute to poor posture.
Strength Training Exercises for Back and Core Support
A strong back and core are essential components for maintaining good posture. Strengthening these muscles provides support for the spine and helps prevent slouching. Below are effective strength training exercises:
- Plank: Holding a plank position engages the entire core, including the back muscles. Aim for 30-60 seconds.
- Bird-Dog: While on all fours, extend one arm and the opposite leg, then switch. This exercise improves balance and engages the core.
- Bridges: Lying on your back with knees bent, lift your hips towards the ceiling, engaging your glutes and lower back.
- Superman Exercise: Lying face down, lift your arms and legs off the ground simultaneously. This strengthens the lower back.
- Wall Sits: Lean against a wall in a sitting position, keeping your back straight. Hold for 20-60 seconds to build endurance in your thigh and core muscles.
Frequency and Duration of Exercises for Optimal Results
To achieve optimal results in maintaining good posture, consistency is key. It is recommended to incorporate stretching exercises at least 2-3 times per week, holding each stretch for 15-30 seconds. For strengthening exercises, a routine of 2-3 sessions per week is ideal, focusing on 2-3 sets of 8-12 repetitions for each exercise. Regularly engaging in these exercises fosters better posture, enhances flexibility, and builds the necessary strength to support daily activities.
By integrating stretching and strengthening into your fitness routine, you can significantly contribute to a healthier, more aligned body.
Mindfulness and Posture Awareness
Developing mindfulness about posture is essential for maintaining good physical health and preventing strain. Being aware of one’s body position throughout the day can significantly reduce discomfort and the risk of musculoskeletal issues. By incorporating mindfulness techniques into daily routines, individuals can enhance their posture awareness and promote a healthier lifestyle.One effective way to develop posture mindfulness is through the practice of intentional breathing, which serves as a foundation for physical awareness.
Proper breathing techniques can influence posture by encouraging relaxation and alignment of the spine. When individuals focus on deep, diaphragmatic breathing, they become more attuned to their body’s positioning and can better maintain a neutral spine.
Techniques for Posture Awareness
To cultivate posture awareness throughout the day, various techniques can be employed. These practices encourage regular self-checks and promote a conscious effort to maintain alignment.
- Mindful Breathing: Engaging in deep breathing exercises allows individuals to reconnect with their body. Inhale deeply through the nose, allowing the abdomen to expand, followed by a slow exhale through the mouth. This practice not only calms the mind but also promotes a natural upright position.
- Regular Reminders: Setting periodic reminders on your phone or using sticky notes around your workspace can prompt self-checks for posture. These visual cues serve as gentle nudges to maintain alignment and can be particularly effective during long periods of sitting.
- Posture Checkpoints: Choosing specific times during the day to assess your posture can be beneficial. For example, when transitioning between tasks or during moments of waiting, take a moment to evaluate your alignment and make adjustments as needed.
- Body Scans: Practicing a body scan meditation involves focusing on different body parts sequentially, starting from the feet and moving upward. This technique allows you to identify areas of tension or misalignment, fostering an understanding of your body’s stance.
- Movement Breaks: Incorporating short, mindful movement breaks throughout the day encourages both physical and mental awareness. Stand up, stretch, and consciously realign your posture. This can help alleviate stiffness and remind you to maintain good posture.
Engaging in these practices consistently can lead to improved posture awareness and a reduction in strain-related discomfort. By combining mindfulness techniques with deep breathing practices, individuals can create a more supportive environment for their bodies. Regularly checking in with oneself not only enhances posture but also promotes a greater sense of well-being and balance in daily life.
Long-term Strategies for Good Posture
Maintaining good posture is not just a short-term goal; it requires a sustained commitment to daily habits that support a healthy alignment of the body. Over time, these strategies can significantly reduce the risk of discomfort and strain associated with poor posture. By incorporating these practices into your routine, you can cultivate an environment conducive to maintaining good posture for years to come.
Daily Habits that Support Good Posture
Establishing daily habits that reinforce good posture is essential for long-term success. These habits can be integrated seamlessly into your existing routine and may include the following:
- Regularly check your posture while sitting, standing, and walking to ensure your spine remains aligned.
- Incorporate reminders in your environment, such as sticky notes or alarms, to prompt you to adjust your posture throughout the day.
- Utilize ergonomic furniture and tools, such as chairs with lumbar support and desks at appropriate heights, to promote a healthy sitting position.
- Practice mindfulness techniques that encourage awareness of your body’s alignment, helping you to physically correct your posture as needed.
- Ensure adequate hydration and nutrition to support overall physical health, which can positively influence muscle function and posture.
Regular Posture Assessments and Adjustments
Implementing regular posture assessments can be beneficial in identifying areas needing improvement. Engaging in periodic evaluations allows for timely adjustments to be made before any potential problems escalate. The advantages of consistent posture assessments include:
- Enhanced awareness of your posture habits, leading to proactive changes.
- Identification of any deviations from ideal posture, which can help in addressing specific weaknesses or imbalances.
- Opportunities to track progress over time, reinforcing positive changes and adjustments.
- Encouragement to seek professional guidance, such as from a chiropractor or physical therapist, to ensure alignment and health.
- Increased motivation to maintain good posture as improvements become evident through assessments.
Motivational Strategies for Commitment to Good Posture Practices
Staying committed to good posture practices can be challenging, but employing motivational strategies can help maintain focus. These strategies can include:
- Setting specific, achievable posture goals and tracking progress in a journal or app.
- Creating a supportive environment by involving friends or family in posture improvement initiatives.
- Rewarding yourself for reaching milestones, such as sustaining good posture for a set period.
- Engaging in group classes or workshops focused on posture, which can foster a sense of community and shared learning.
- Visualizing the long-term benefits of good posture, such as reduced pain, increased energy, and improved confidence, to reinforce your commitment.
Final Summary

In conclusion, maintaining good posture is a vital aspect of our daily lives that should not be overlooked. By understanding the causes of poor posture and implementing the techniques discussed, individuals can significantly reduce strain and improve their overall health. Adopting long-term strategies, such as regular posture assessments and mindful practices, fosters a commitment to well-being. Let us embrace these practices as we strive for a healthier, more balanced lifestyle, ensuring that good posture becomes an integral part of our daily routines.